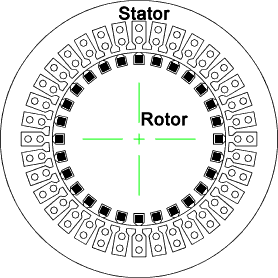
Construction of Alternator
An alternator consists of:
-> stator & rotor
Stator:
§ Stator is the stationary part of the alternator and contains 3-phase armature windings. Stator core is built up of silicon steel laminations to reduce eddy current losses. The laminations are provided with slots on its inner periphery and are packed tightly together by cast iron frame.
§ Open slots are used allowing easy installation of stator coils and easy removal in case of repair. Coils are insulated before inserting in the slots and are further protected by fiber.
§ The three phase windings are placed in these slots and serves as the armature windings of the alternator. The armature windings are always connected in star and the neutral is connected to ground.
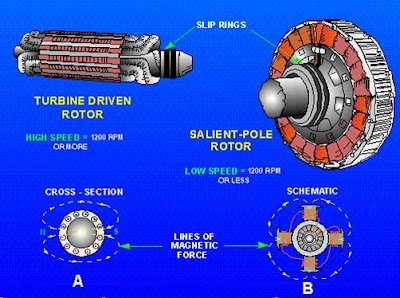
Rotor:
§ The rotor is rotating part of the alternator. It carries a field winding which is supplied with dc current through two slip rings by a separate dc source. This dc source (exciter) is generally a small dc generator mounted on the shaft of the alternator.
§ There are two types of rotors:
-> Salient pole type rotor
-> non-salient pole type rotor.
Salient pole Alternator:
§ Salient means sticking out or projected out. A salient pole is a magnetic pole that is projected out of the rotor surface.
§ The salient pole alternators are slow-speed machines, speed varying from 150 to 600 rpm. These alternators are driven by hydraulic turbines. They are also called water-wheel generators or hydro-generators. Pelton wheel, Francis turbine and Kaplan turbine are types of hydraulic turbines used with these alternators:
§ Salient type rotor has large diameter, small length and low speed. Diameter is usually between 3-15 m.
§ Salient type rotor has non-uniform air-gap and two or four poles.
§ Low and medium speed alternators (120 – 400 rpm) driven by diesel engines or water turbines have salient pole type rotors due to following reasons:
o The salient field poles would cause an excessive windage loss if driven at high speed and would tend to produce noise.
o Salient-pole construction can not be made strong enough to withstand the mechanical stress at higher speeds.
Non-Salient pole Alternator:
§ Non-salient pole is non-projecting surface type.
§ Non-salient type rotor has small diameter and large length.
§ Non-salient type rotor is used for high speed and has uniform air-gap.
§ Non-salient pole rotors have four or more poles.
§ High speed alternators (1500 – 3000 rpm) are driven by steam turbines and use non-salient type rotors due to following reasons:
o Gives noiseless operation at high speeds.
o Flux is uniformly distributed along the periphery, so proper sine wave is obtained which gives better emf.







I really liked your article , your article is very
ReplyDeletepetrified me in the learning process and provide
additional knowledge to me , maybe I can learn
more from you, you can also check out http://crbtech.in/Electrical-Training/index.php/2017/08/03/alternator-synchronous-generator-and-its-types/ which is also a very good blog
very little or no voltage and power transformers ar at intervals the foremost used in low voltage electrical and electronic circuit designs tend to use copper conductors and it's have succeeding mechanical strength and smaller conductor size than same Al sections.Iron Powder Cores
ReplyDeleteTransformer winding is else an additional main section of a tool construction, as a results of this could otherwise be the foremost necessary current carrying conductors wound round the core ring. If the first input voltage is larger than the secondary output voltage, the device is termed as a steo down device. If the first input voltage ar nearly be a smaller amount than the secondary output voltage, the device is termed as intensify device.toroidal transformer winding machine
ReplyDeleteAl wire is low value and lighter than the copper wire, that picks associate honest larger cross sectional house of conductor accustomed carry the massive quantity of current, so it's at intervals the foremost utilized in broad power device applications.Coil Winding
ReplyDelete